How does society fill jobs that no one wants to do? One choice is that you can pay workers in these positions extremely well, making these hard jobs desirable. That is expensive, making it hard or impossible to turn a profit. The other option is to coerce people into performing that labor – through financial, legal, or violent means… In which way did landowners in colonial America solve this dilemma?
This lesson was reported from:
A chapter of The United States: An Open Ended History, a free online textbook. Adapted in part from open sources.
For Your Consideration:
- What was indentured servitude? What kind of rules governed the lives of servants?
- Briefly describe the transatlantic slave trade.
- Identify two ways in which slavery was different from indentured servitude.
- How did slaves resist their masters?
- What was Bacon’s Rebellion?
Indentured Servitude
Indentured servitude was a system by which immigrants, typically young Europeans under 25, both men and women, came to the English colonies.
Farmers, merchants, and shopkeepers in the British colonies found it very difficult to hire free workers, primarily because it was easy for potential workers to set up their own farms by moving to frontier lands. Consequently, a common solution was to transport a young worker from Britain or a German state, who would work for several years to pay off the debt of their travel costs. During the indenture period the servants were not paid cash wages, but were provided with food, accommodation, clothing and training. The indenture document specified how many years the servant would be required to work, after which they would be free. Terms of indenture ranged from one to seven years with typical terms of four or five years.

Servants could not marry without the permission of their owner, were subject to physical punishment (like many young ordinary servants), and saw their obligation to labor enforced by the courts. To ensure uninterrupted work by the female servants, the law lengthened the term of their indenture if they became pregnant. But unlike slaves, servants were guaranteed to be eventually released from bondage. At the end of their term they received a payment known as “freedom dues” (typically a small parcel of land or a new suit of clothes) and become free members of society. One could buy and sell indentured servants’ contracts, and the right to their labor would change hands, but not the person as a piece of property.
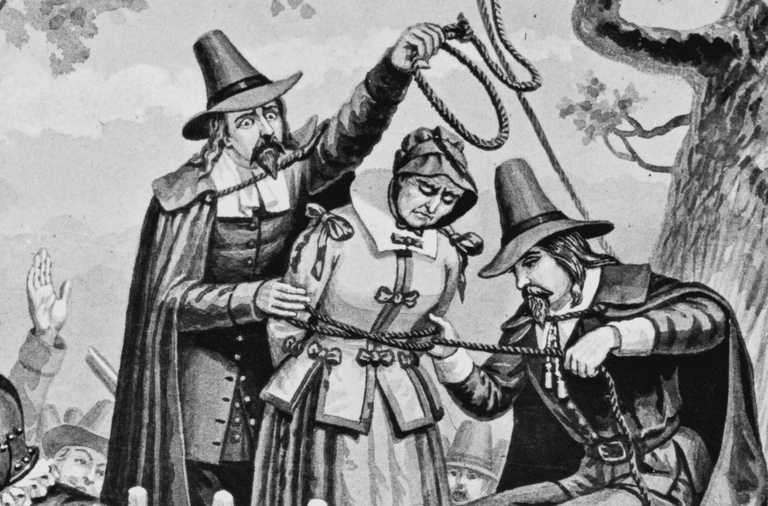
Both male and female laborers could be subject to violence, occasionally even resulting in death. Historian Richard Hofstadter notes that, as slaves arrived in greater numbers after 1700, white laborers in Virginia became a “privileged stratum, assigned to lighter work and more skilled tasks.” He also notes that “Runaways were regularly advertised in the newspapers, rewards were offered, and both sheriffs and the general public were enlisted to secure their return. … The standard penalty in the North, not always rigorously enforced, was extra service of twice the time the master had lost, though whipping was also common.”

Transatlantic Slave Trade

The transatlantic slave trade was the forced transportation of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were enslaved and transported in the transatlantic slave trade were Africans from central and western Africa, who had been sold by other West Africans to Western European slave traders (with a small number being captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids), who brought them to the Americas. South Atlantic and Caribbean economies especially were dependent on the supply of secure labor for the production of commodity crops such as tobacco, sugar, and cotton to sell elsewhere in the colonies and in Europe.
The duration of the transatlantic voyage varied widely, from one to six months depending on weather conditions. The journey became more efficient over the centuries; while an average transatlantic journey of the early 16th century lasted several months, by the 19th century the crossing often required fewer than six weeks.
It is believed that African kings, warlords and private kidnappers sold captives to Europeans who held several coastal forts. The captives were usually force-marched to these ports along the western coast of Africa, where they were held for sale to the European or American slave traders. Typical slave ships contained several hundred slaves with about 30 crew members.

The male captives were normally chained together in pairs to save space; right leg to the next man’s left leg — while the women and children may have had somewhat more room. At best, captives were fed beans, corn, yams, rice, and palm oil. Slaves were typically fed one meal a day with water, if at all.
 Slaves lived below the decks in conditions of squalor and indescribable horror. Disease spread and ill health was one of the biggest killers. Mortality rates were high, and death made conditions even worse. Many crew members avoided going into the hold because of the smell, the sights, and the sounds below deck. Even though the corpses were thrown overboard, living slaves might be shackled for hours and sometimes days to someone who was dead.
Slaves lived below the decks in conditions of squalor and indescribable horror. Disease spread and ill health was one of the biggest killers. Mortality rates were high, and death made conditions even worse. Many crew members avoided going into the hold because of the smell, the sights, and the sounds below deck. Even though the corpses were thrown overboard, living slaves might be shackled for hours and sometimes days to someone who was dead.
Current estimates are that about 12 million Africans were shipped across the Atlantic, although the number purchased by the traders was considerably higher, as the passage had a high death rate. Disease and starvation due to the length of the passage were the main contributors to the death toll, as diseases spread rapidly in the close-quarter compartments of the slave ships.
As a way to counteract disease, slaves were forced onto the deck of the ship for exercise. This frequently resulted in beatings from the crew because the slaves would be unwilling to dance for them or interact. These beatings would often be severe and could result in the slave dying or becoming more susceptible to diseases.
Slaves resisted in many ways. The two most common types of resistance were refusal to eat and suicide. Suicide was a frequent occurrence, often by refusal of food or medicine or jumping overboard, as well as by a variety of other opportunistic means.
Ottobah Cugoano, who was taken from Africa as a slave when he was a child, later wrote a book of his life and in it described an uprising aboard the ship on which he was transported to the West Indies:
“When we found ourselves at last taken away, death was more preferable than life, and a plan was concerted amongst us, that we might burn and blow up the ship, and to perish all together in the flames.”
Slave ships were designed and operated to prevent the slaves from revolting. Resistance among slaves usually ended in failure and participants in a rebellion were punished severely. Despite this, about one out of ten ships experienced some sort of rebellion.
Slavery
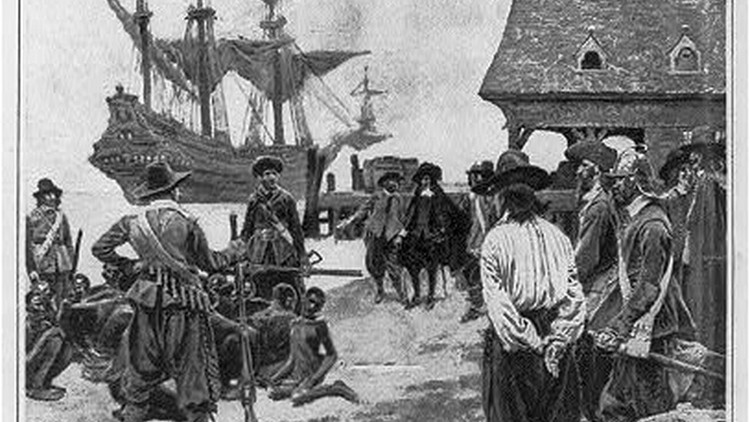
The first Africans to be brought to British North America landed in Virginia in 1619. They arrived on a Dutch ship that had captured them from the Spanish. These approximately 20 individuals appear to have been treated as indentured servants, and a significant number of enslaved Africans earned freedom by fulfilling a work contract or for converting to Christianity. Like European indentured servants at the completion of their contract, many of these first African Americans were each granted 50 acres (200,000 m2) of land when freed from their indentures, so they could raise their own tobacco or other crops.
By 1650, there were about 300 Africans living in Virginia, about 1% of an estimated 30,000 population of people of English and European ancestry. Some successful free people of color, such as Anthony Johnson, in turn acquired slaves or indentured servants for workers. Some historians say this evidence suggests that racial attitudes were much more flexible in 17th-century Virginia than they would later become.
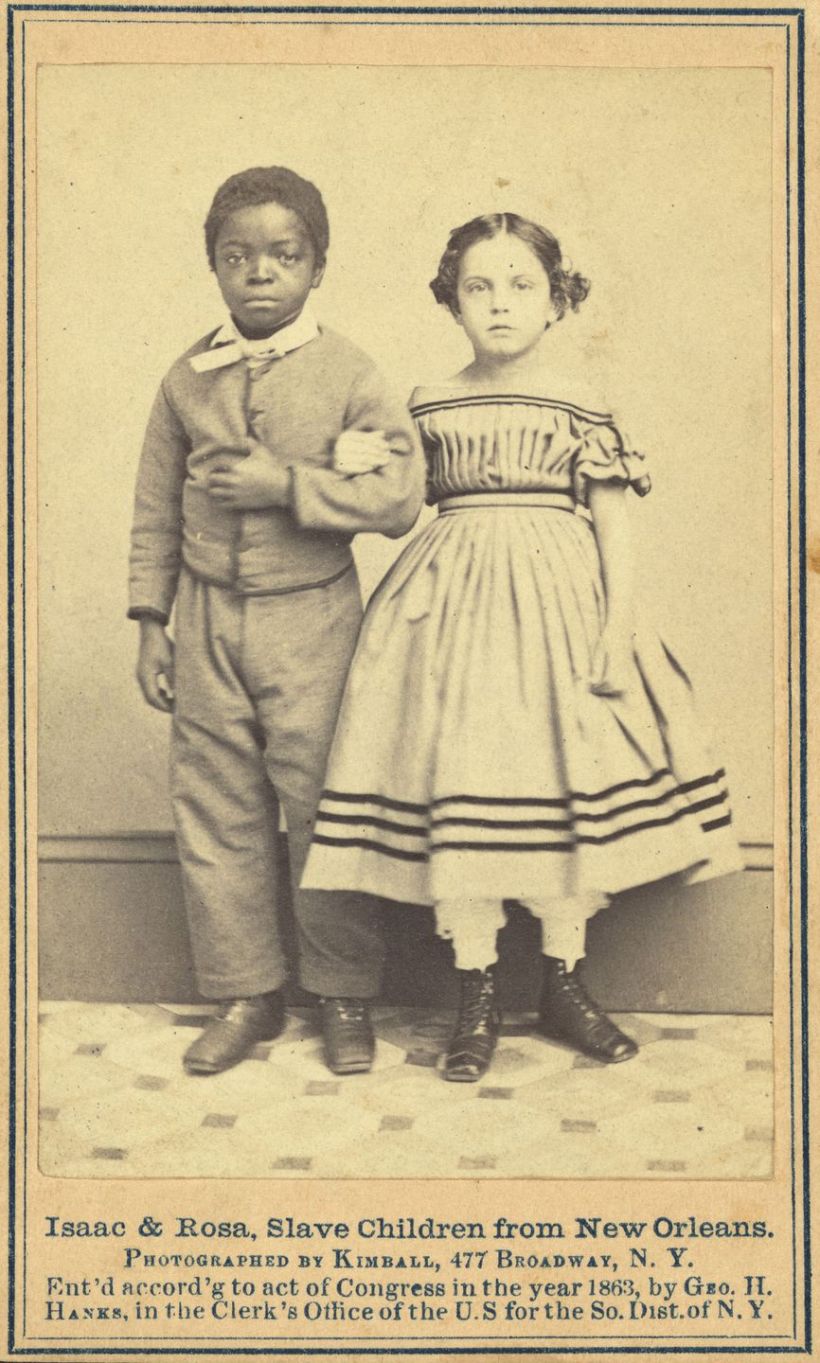
 From this early start, American slavery was born. Slavery was an institution that lasted for more than three hundred years under which African Americans could expect to be held for life as the property of their masters. This system evolved over time, gradually becoming more strict and regulated. It also varied from owner to owner – some masters may have been more gentle or cruel than others, more generous or stingy with food, etc… But at the end of the day, an enslaved person was regarded by the law as little more than a piece of livestock – property that was totally at the mercy, or lack thereof, of their master.
From this early start, American slavery was born. Slavery was an institution that lasted for more than three hundred years under which African Americans could expect to be held for life as the property of their masters. This system evolved over time, gradually becoming more strict and regulated. It also varied from owner to owner – some masters may have been more gentle or cruel than others, more generous or stingy with food, etc… But at the end of the day, an enslaved person was regarded by the law as little more than a piece of livestock – property that was totally at the mercy, or lack thereof, of their master.
In the 1660s, the colonial legislature adopted a law stating that all children born in the colony would take the status of their mothers, regardless of who their father was. Thus children born to enslaved mothers would be enslaved, regardless of their ethnicity or paternity. This was contrary to English common law for children of parents who are both English subjects, in which the child takes status from the father. But the law also meant that mixed-race children born to white women were born free, and many families of free African Americans were descended from unions between white women and ethnic African men during the colonial era.
Slavery became a racial caste – a status determined at birth, for life.
You can see this process for yourself – Primary Source Analysis: The Evolution of the Virginia Laws of Servitude and Slavery (1643-1691).

During the early 17th century, Virginia planters developed the commodity crop of tobacco as their chief export. It was a labor-intensive crop, and demand for it in England and Europe led to an increase in the importation of African slaves in the colony. By the mid-eighteenth century, there were 145,000 slaves in the Chesapeake Bay region, spread mostly on large plantations, as compared to 50,000 in the Spanish colony of Cuba, where they worked in urbanized settlements.

The treatment of slaves in the varied by time and place, but was generally nothing that you would wish to experience – slavery was brutal and degrading. Slaves were punished by whipping, shackling, beating, mutilation, branding and/or imprisonment. Punishment was most often meted out in response to disobedience or perceived infractions, but masters or overseers sometimes abused slaves to assert dominance.
An 1850 publication provided slaveholders with guidance on how to produce the “ideal slave:”
- Maintain strict discipline and unconditional submission.
- Create a sense of personal inferiority, so that slaves “know their place.”
- Instill fear.
- Teach servants to take interest in their master’s enterprise.
- Deprive access to education and recreation, to ensure that slaves remain uneducated, helpless, and dependent.

Under slavery, planters and other slaveholders owned, controlled and sold entire families of slaves. The slave population increased in the southern United States as native-born slaves produced large families. Slaves were at a continual risk of losing family members if their owners decided to sell them for profit, punishment or to pay debts. Slaveholders also made gifts of slaves to grown children (or other family members), such as on the occasion of their marriage. Masters considered slave children ready to work and leave home as young as age 12 or 14.
A few slaves retaliated by murdering their owners and overseers, burning barns, and killing horses. These acts were rare, however, given the strong, harsh reactions from neighboring whites who worried that any act of defiance might lead to a full-scale slave rebellion. Work slowdowns were probably the most frequent form of resistance and hard to control – slaves deliberately worked at a pace fast enough not to get in trouble, but no faster.

Bacon’s Rebellion
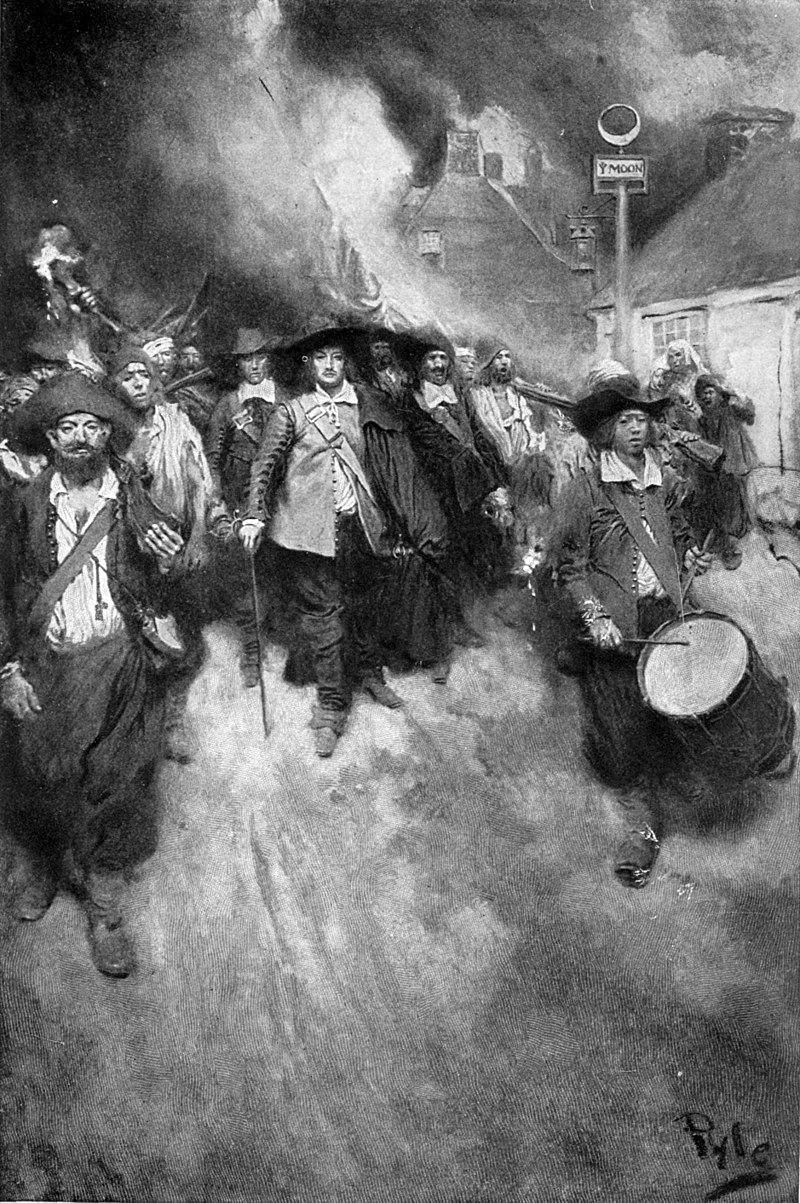

Bacon’s Rebellion was an armed rebellion in 1676 by Virginia settlers led by Nathaniel Bacon against the rule of Royal Governor William Berkeley. The governor’s dismissive policy with regard to land on its western frontier, along with other challenges including leaving Bacon out of his inner circle, refusing to allow Bacon to be a part of his fur trade with the Native Americans, and a lack of colonial response to Doeg American Indian attacks, helped to motivate a popular uprising against Berkeley, who had failed to address the demands of the colonists regarding their safety.
A thousand Virginians of all classes and races rose up in arms against Berkeley, attacking Indians, chasing Berkeley from Jamestown, Virginia, and ultimately torching the capital. The rebellion was first suppressed by a few armed merchant ships from London whose captains sided with Berkeley and the loyalists. Government forces from England arrived soon after and spent several years defeating pockets of resistance and reforming the colonial government to be once more under direct royal control.
It was the first rebellion in the American colonies in which discontented frontiersmen took part. The alliance between indentured servants and Africans (most enslaved until death or freed), united by their bond-servitude, disturbed the ruling class, who responded by hardening the racial caste of slavery in an attempt to divide the two races from subsequent united uprisings with the passage of the Virginia Slave Codes of 1705. While the farmers did not succeed in their initial goal of driving the Indians from Virginia, the rebellion did result in Berkeley being recalled to England.
The article was adapted in part from:











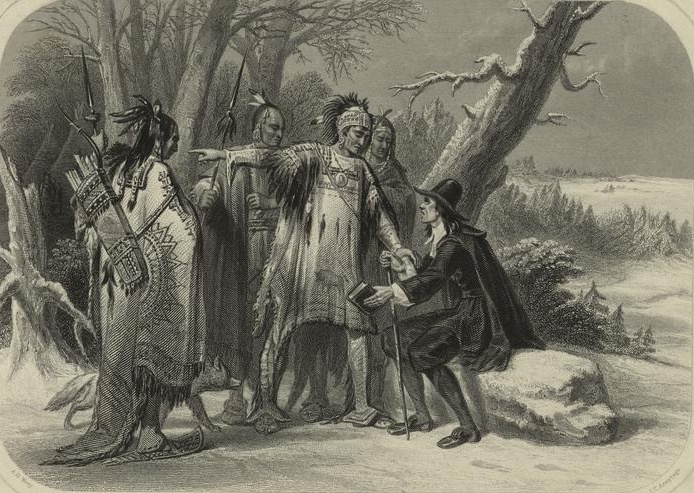
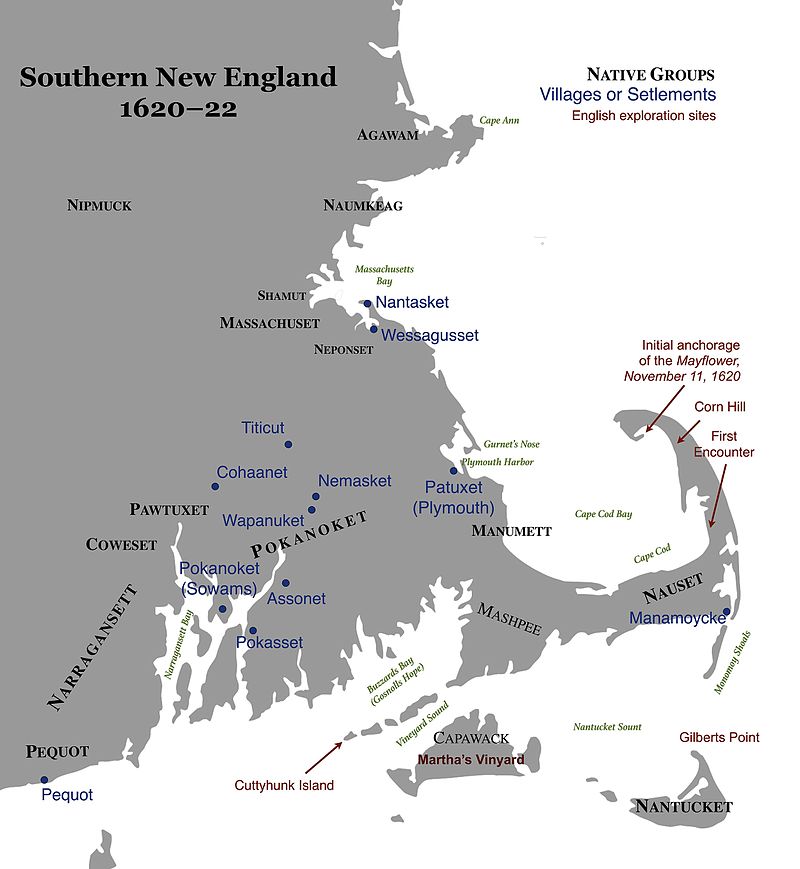 When the Mayflower landed in 1620, Squanto worked to broker peaceable relations between the Pilgrims and the local Pokanokets (a subgroup within the Wampanoag’s orbit). He played a key role in the early meetings in March 1621, partly because he spoke English. He then lived with the Pilgrims for 20 months, acting as a translator, guide, and adviser. He introduced the settlers to the fur trade, and taught them how to sow and fertilize native crops, which proved vital since the seeds which the Pilgrims had brought from England largely failed. Whatever his motivations, with great kindness and patience, Squanto taught the English the skills they needed to survive, including how best to cultivate varieties of the Three Sisters: beans, maize and squash.
When the Mayflower landed in 1620, Squanto worked to broker peaceable relations between the Pilgrims and the local Pokanokets (a subgroup within the Wampanoag’s orbit). He played a key role in the early meetings in March 1621, partly because he spoke English. He then lived with the Pilgrims for 20 months, acting as a translator, guide, and adviser. He introduced the settlers to the fur trade, and taught them how to sow and fertilize native crops, which proved vital since the seeds which the Pilgrims had brought from England largely failed. Whatever his motivations, with great kindness and patience, Squanto taught the English the skills they needed to survive, including how best to cultivate varieties of the Three Sisters: beans, maize and squash.












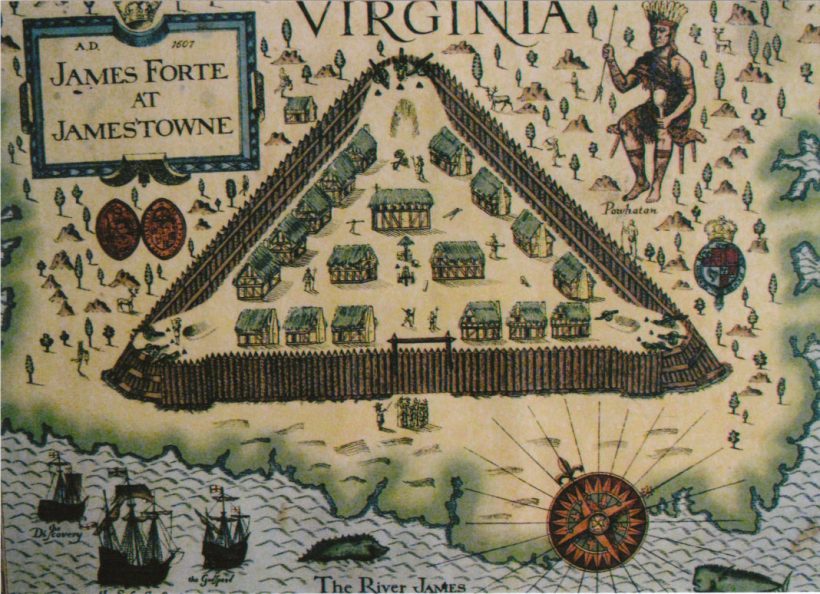 The area laid out in the royal charter was named Virginia, after both the organizing Virginia Company of London and Queen Elizabeth, “the Virgin Queen.” Founded in 1607, the first settlement – a small triangular fort populated by about 100 settlers at the mouth of the James River – was named after King James I. Jamestown was the first permanent English colony in the Americas.
The area laid out in the royal charter was named Virginia, after both the organizing Virginia Company of London and Queen Elizabeth, “the Virgin Queen.” Founded in 1607, the first settlement – a small triangular fort populated by about 100 settlers at the mouth of the James River – was named after King James I. Jamestown was the first permanent English colony in the Americas.
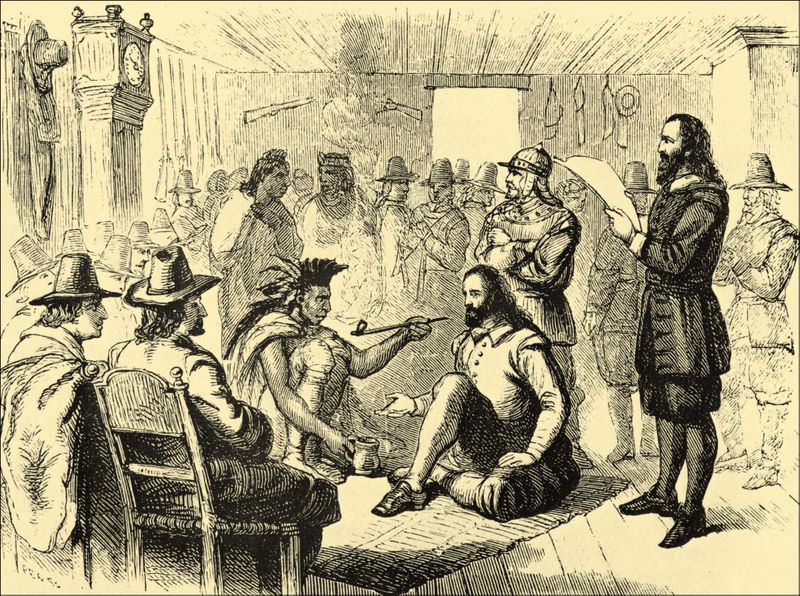
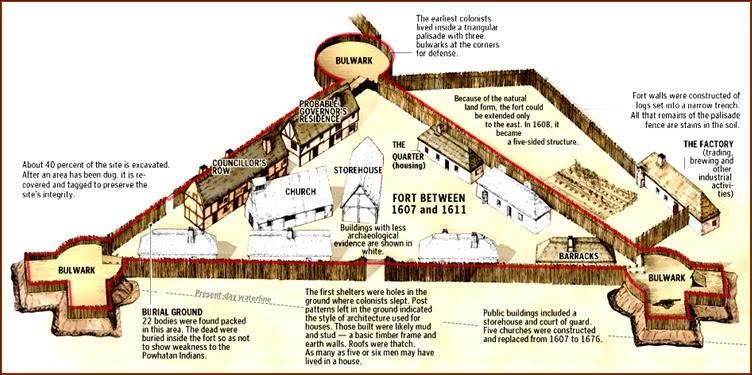 Two men helped the colony to survive: adventurer John Smith and businessman John Rolfe. Smith, who arrived in Virginia in 1608, introduced an ultimatum: “He that will not work, shall not eat”, equivalent to the 2nd Thessalonians 3:10 in the Bible. Under this dire threat, the colonists at last learned how to raise crops and trade with the nearby Indians, with whom Smith had made peace.
Two men helped the colony to survive: adventurer John Smith and businessman John Rolfe. Smith, who arrived in Virginia in 1608, introduced an ultimatum: “He that will not work, shall not eat”, equivalent to the 2nd Thessalonians 3:10 in the Bible. Under this dire threat, the colonists at last learned how to raise crops and trade with the nearby Indians, with whom Smith had made peace.


















































































You must be logged in to post a comment.