This lesson was reported from:
A chapter of The United States: An Open Ended History, a free online textbook. Adapted in part from open sources.
For Your Consideration:
-
Why did the Mexican government encourage Americans to move to Texas? What caused these Americans to revolt against Mexico?
-
What was Manifest Destiny? Did all people at the time agree with this idea?
-
Why didn’t Texas immediately join the United States?
-
How did the Mexican-American War begin?
-
Why did a number of Northerners – such as Henry David Thoreau, John Quincy Adams, and Frederick Douglass – oppose the war?
-
What did the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo do?
Texas

Mexico obtained independence from Spain in 1821, and briefly experimented with monarchy, becoming a republic in 1824. This early period of Mexican history was characterized by considerable instability. In the 1820s and 30s, the northern Mexican region of Texas was very sparsely populated, with fewer than 3,500 non-Native American residents, and only about 200 soldiers, which made it extremely vulnerable to attacks by the Comanche, Apache, and Navajo – who also claimed the land as their own. These indigenous people, especially the Comanche, took advantage of the weakness of the newly independent Mexico to undertake large-scale raids over hundreds of miles against Mexican targets to acquire livestock for their own use and to supply an expanding market in Texas and the US.
In the hopes that an influx of settlers could control the Indian raids, the bankrupt Mexican government liberalized immigration policies for the region. Finally able to settle legally in Texas, Americans from the United States soon vastly outnumbered the Tejanos, or Mexican citizens of Texas. Most of the immigrants came from the southern United States. Many were slave owners, and most brought with them significant prejudices against other races, attitudes often applied to the Tejanos.
Mexican authorities became increasingly concerned about the stability of the region – now because of the Americans in their midst. After Mexico abolished slavery in 1829, the American population in Texas teetered on the brink of revolt. Alarmed, the Mexican government implemented a new round of restrictions, which, among other things, prohibited further immigration to Texas from the United States, increased taxes, and reiterated the ban on slavery. Settlers simply circumvented or ignored the laws. By 1834, an estimated 30,000 Americans lived in Texas, compared to only 7,800 Mexican-born residents. By the end of 1835, almost 5,000 enslaved Africans and African Americans lived in Texas, making up 13 percent of the non-Indian population.

The Republic of Texas declared independence from the Republic of Mexico on March 2, 1836. At the time the vast majority of the population favored the annexation of the Republic by the United States. Fearing a repeat of the Missouri crisis, the leadership of both major U.S. political parties, the Democrats and the Whigs, opposed the introduction of Texas, a vast slave-holding region, into the volatile political climate of the pro- and anti-slavery sectional controversies in Congress. Moreover, they wished to avoid a war with Mexico, whose government refused to acknowledge the sovereignty of its rebellious northern province.
Manifest Destiny
For individual settlers, the decision to move west was typically driven by the desire for economic opportunity. But how did Americans justify their right to take lands from Native Americans, Mexicans, and others who might already live in the west?
In the 19th century, manifest destiny was a widely held belief in the United States that its settlers were destined to expand across the entire continent of North America. A term coined by journalist John L. O’Sullivan in 1845 to describe a set of attitudes that had already existed for some time before, there are three basic themes to manifest destiny:
- the virtue of the American people and their institutions;
- the mission to spread these institutions, thereby redeeming and remaking the world in the image of the United States;
- the destiny under God to do this work.
O’Sullivan wrote: “And that claim is by the right of our manifest destiny to overspread and to possess the whole of the continent which Providence has given us for the development of the great experiment of liberty and federated self-government entrusted to us.”

Ironically, O’Sullivan’s term became popular only after it was criticized by Whig opponents of the Polk administration. On January 3, 1846, Representative Robert Winthrop ridiculed the concept in Congress, saying “I suppose the right of a manifest destiny to spread will not be admitted to exist in any nation except the universal Yankee nation.” Winthrop was the first in a long line of critics who suggested that advocates of manifest destiny were citing “Divine Providence” for justification of actions that were motivated by chauvinism and self-interest. Despite this criticism, expansionists embraced the phrase, which caught on so quickly that its origin was soon forgotten.
The Mexican-American War
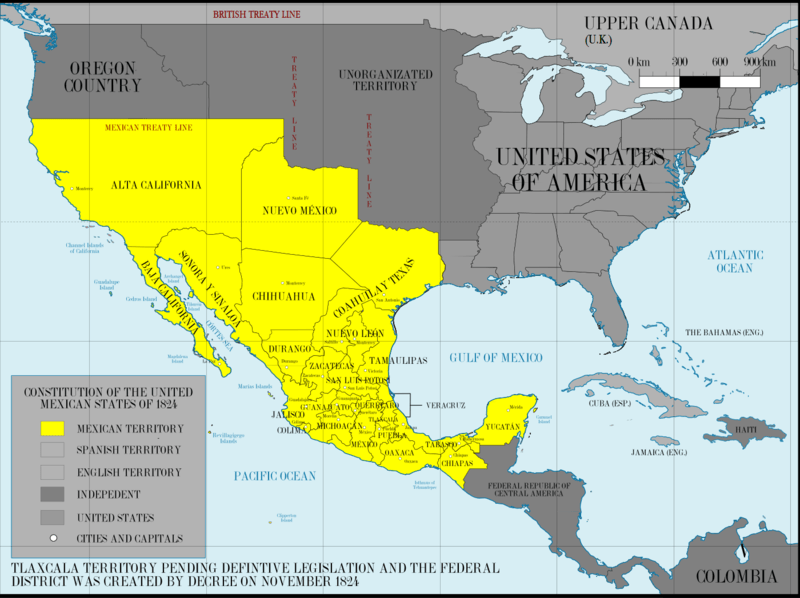
For almost a decade, Texas remained an independent republic, largely because its annexation as a huge new slave state would disrupt the increasingly precarious balance of political power in the United States. In 1845, President James K. Polk, narrowly elected on a platform of westward expansion, brought the Republic of Texas into the Union as the 28th state. Polk’s move was the first gambit in a larger design. Texas claimed that its border with Mexico was the Rio Grande River; Mexico argued that the border stood 150 miles to the north along the Nueces River. Meanwhile, American settlers were flooding into the territories of New Mexico and California, citing manifest destiny as their justification to do so.

U.S. attempts to purchase from Mexico the New Mexico and California territories failed. In 1846, President Polk ordered General Taylor and his forces south to the Rio Grande, entering deep into the territory that Mexico claimed as their own.
Regarding the beginning of the war, Ulysses S. Grant, who had opposed the war but served as an army lieutenant in Taylor’s Army, claims in his Personal Memoirs (1885) that the main goal of the U.S. Army’s advance from Nueces River to Rio Grande was to provoke the outbreak of war without attacking first – to make the whole war seem defensive, rather than as a war of conquest against a weaker nation.
“We were sent to provoke a fight, but it was essential that Mexico should commence it. It was very doubtful whether Congress would declare war; but if Mexico should attack our troops, the Executive could announce, “Whereas, war exists by the acts of, etc.,” and prosecute the contest with vigor. Once initiated there were but few public men who would have the courage to oppose it….
Mexico showing no willingness to come to the Nueces to drive the invaders from her soil, it became necessary for the ‘invaders’ to approach to within a convenient distance to be struck. Accordingly, preparations were begun for moving the army to the Rio Grande… It was desirable to occupy a position near the largest centre of population possible to reach, without absolutely invading territory to which we set up no claim whatever.
Eleven American soldiers were killed in this initial conflict, provoked by the Americans. Just as Grant described, Polk claimed the need to avenge the honor of these fallen men and pushed for open warfare against Mexico – a full invasion by the better equipped, better organized U.S. army commenced. His message to Congress on May 11, 1846, claimed that “Mexico has passed the boundary of the United States, has invaded our territory and shed American blood upon American soil.”
American troops occupied the lightly populated territory of New Mexico, then supported a revolt of settlers in California. A U.S. force under Zachary Taylor invaded Mexico, winning victories at Monterrey and Buena Vista, but failing to bring the Mexicans to the negotiating table.
Mexico was not inclined nor able to negotiate. In 1846 alone, the presidency changed hands four times, the war ministry six times, and the finance ministry sixteen times. Mexican public opinion and all political factions agreed that selling the territories to the United States would tarnish the national honor. Mexicans who opposed direct conflict with the United States were viewed as traitors.

Opposition to the War
In the United States, increasingly divided by sectional rivalry, the war was a partisan issue. Most Whigs in the North and South opposed it; most Democrats supported it. Southern Democrats supported it in hope of adding slave-owning territory to the South and avoiding being overwhelmed in the Senate by the faster-growing North.
Northern antislavery elements feared the expansion of the Southern Slave Power; Whigs generally wanted to strengthen the economy with industrialization, not expand it with more land. Among the most vocal opposing the war in the House of Representatives was John Quincy Adams of Massachusetts. Adams had first voiced concerns about expanding into Mexican territory in 1836 when he opposed Texas annexation. He continued this argument in 1846 for the same reason. War with Mexico would add new slavery territory to the nation. When the vote to go to war with Mexico came to a vote on May 13, Adams spoke a resounding “No!” in the chamber. Only 13 others followed his lead.

Northern abolitionists attacked the war as an attempt by slave-owners to strengthen the grip of slavery and thus ensure their continued influence in the federal government. Prominent artists and writers opposed the war.
The Transcendentalist writers Henry David Thoreau and Ralph Waldo Emerson attacked the popular war. Thoreau, who served jail time for refusing to pay his taxes in opposition, composed an essay on how to resist such a large-scale injustice as the war. That essay is now known as Civil Disobedience. Emerson was succinct, predicting that, “The United States will conquer Mexico, but it will be as a man who swallowed the arsenic which brings him down in turn. Mexico will poison us.” Events proved him right, as arguments over the expansion of slavery in the lands seized from Mexico would fuel the drift to civil war just a dozen years later.
Democratic Representative David Wilmot introduced the Wilmot Proviso, which would prohibit slavery in new territory acquired from Mexico. Wilmot’s proposal passed the House but not the Senate, and it spurred further hostility between the factions.
The End of the War
The Battle of Chapultepec was an encounter between the Mexican Army and the United States on the castle of Chapultepec which sits high atop a cliff. At this time, this castle was a renowned military school. After the battle, which ended in the American capture of Mexico City, the legend of “Los Niños Héroes” was born. Although the story is unconfirmed by historians, six military cadets between the ages of 13 and 17 are said to have stayed in the school instead of evacuating, choosing instead to stand their ground for the honor of Mexico. Rather than surrender to the U.S. Army, some of military cadets leaped from the castle walls. One cadet wrapped himself in the Mexican flag and jumped to his death. These Niños Héroes (hero children) became icons in Mexico’s pantheon of heroes.
Outnumbered militarily and with many of its large cities occupied, Mexico could not defend itself; the country was also faced with many internal divisions. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed on February 2, 1848, ended the war. The treaty gave the U.S. undisputed control of Texas, established the U.S.-Mexican border at the Rio Grande, and ceded to the United States the present-day states of California, Nevada, and Utah, most of New Mexico, Arizona, and Colorado, and parts of Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Wyoming (together, so-called Mexican Cession). In return, Mexico received $15 million (approximately $424 million today) – less than half the amount the U.S. had attempted to offer Mexico for the land before the opening of hostilities.
The acquisition was a source of controversy, especially among U.S. politicians who had opposed the war from the start. A leading antiwar U.S. newspaper, the Whig National Intelligencer, sardonically concluded that “We take nothing by conquest … Thank God.”

Before ratifying the treaty, the U.S. Senate made two modifications: changing the wording of Article IX (which guaranteed Mexicans living in the purchased territories the right to become U.S. citizens) and striking out Article X (which conceded the legitimacy of land grants made by the Mexican government). As a result, the majority of Mexicans who suddenly found themselves living in the United States would come to be considered foreigners in their own home and would ultimately lose their land to American settlers who flooded the Mexican Cession over the next generation.

The war was a decisive event for the U.S., marking a significant waypoint for the nation as a growing military power, and a milestone in the U.S. narrative of Manifest Destiny. The war did not resolve the issue of slavery in the U.S. but rather in many ways inflamed it, as potential westward expansion of the institution of slavery became an increasingly central and heated theme in national debates preceding the American Civil War. By extending the nation from coast to coast, the Mexican–American War was a next step in the huge migrations to the West of Americans, which culminated in transcontinental railroads and the Indian wars later in the same century.
The military defeat and loss of territory was a disastrous blow to Mexico, causing the country to enter a period of self-examination as its leaders sought to identify and address the reasons that had led to such a debacle. The war remains a painful historical event for the country.
In Mexico City’s Chapultepec Park, the Niños Héroes (Monument to the Heroic Cadets) commemorates the heroic sacrifice of the six teenaged military cadets who fought to their deaths rather than surrender to American troops during the Battle of Chapultepec Castle. The monument is an important patriotic site in Mexico. On March 5, 1947, nearly one hundred years after the battle, U.S. President Harry S. Truman placed a wreath at the monument and stood for a moment of silence.
The United States has no national memorial to the war, which remains largely unknown to most Americans.
The article was adapted in part from:






























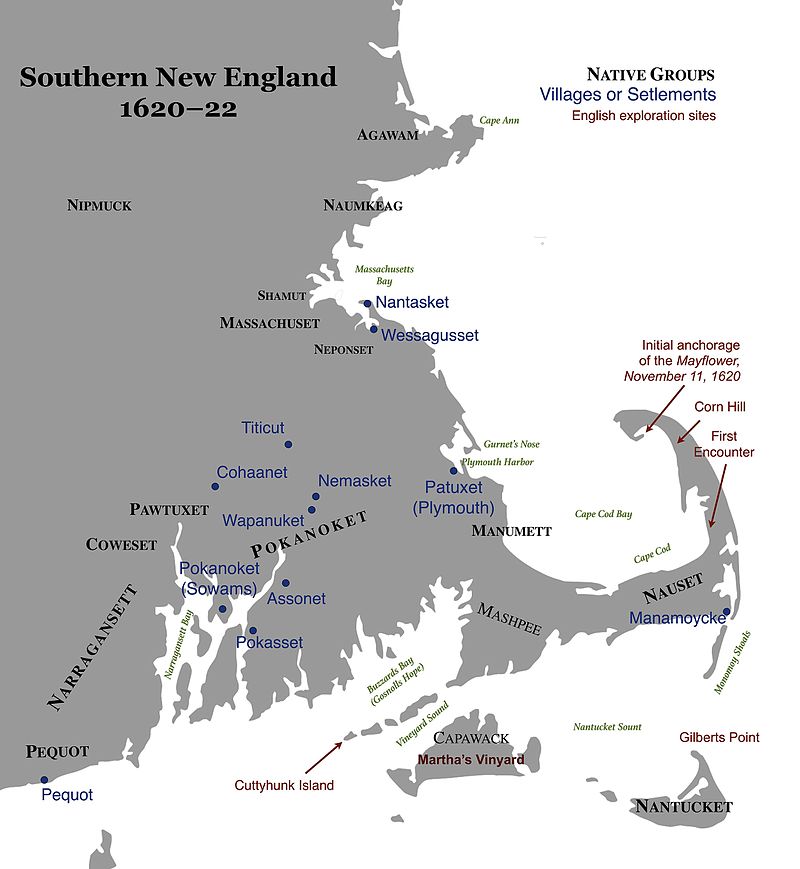 When the Mayflower landed in 1620, Squanto worked to broker peaceable relations between the Pilgrims and the local Pokanokets (a subgroup within the Wampanoag’s orbit). He played a key role in the early meetings in March 1621, partly because he spoke English. He then lived with the Pilgrims for 20 months, acting as a translator, guide, and adviser. He introduced the settlers to the fur trade, and taught them how to sow and fertilize native crops, which proved vital since the seeds which the Pilgrims had brought from England largely failed. Whatever his motivations, with great kindness and patience, Squanto taught the English the skills they needed to survive, including how best to cultivate varieties of the Three Sisters: beans, maize and squash.
When the Mayflower landed in 1620, Squanto worked to broker peaceable relations between the Pilgrims and the local Pokanokets (a subgroup within the Wampanoag’s orbit). He played a key role in the early meetings in March 1621, partly because he spoke English. He then lived with the Pilgrims for 20 months, acting as a translator, guide, and adviser. He introduced the settlers to the fur trade, and taught them how to sow and fertilize native crops, which proved vital since the seeds which the Pilgrims had brought from England largely failed. Whatever his motivations, with great kindness and patience, Squanto taught the English the skills they needed to survive, including how best to cultivate varieties of the Three Sisters: beans, maize and squash.
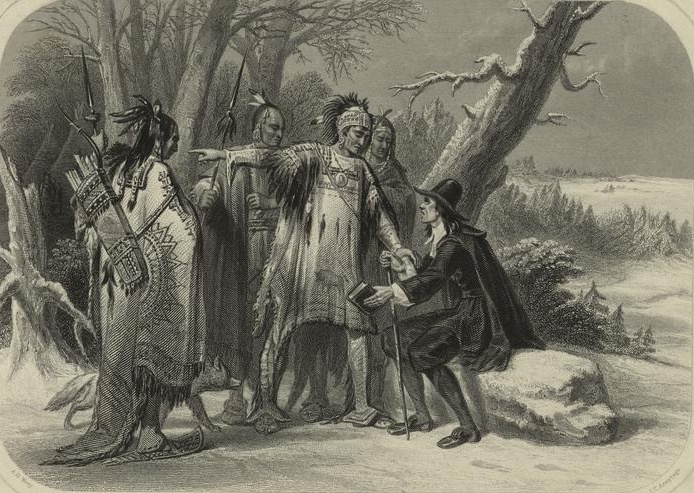
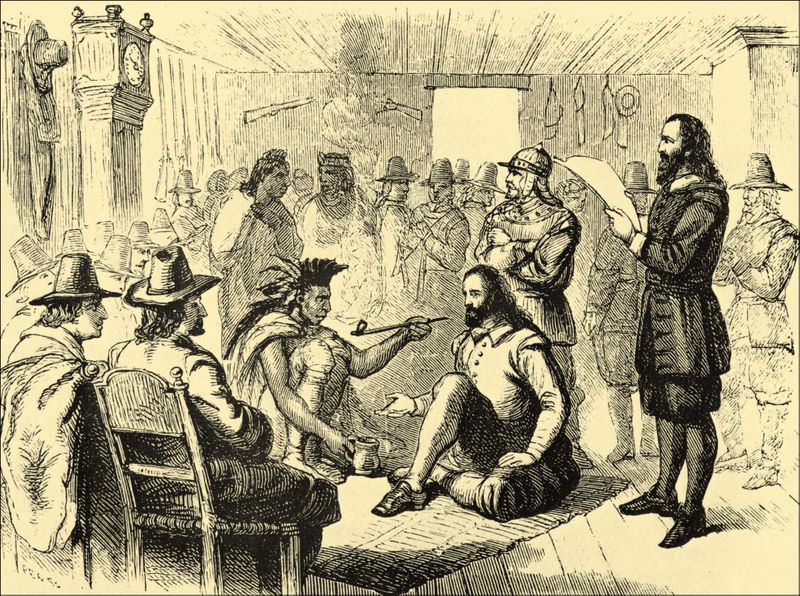












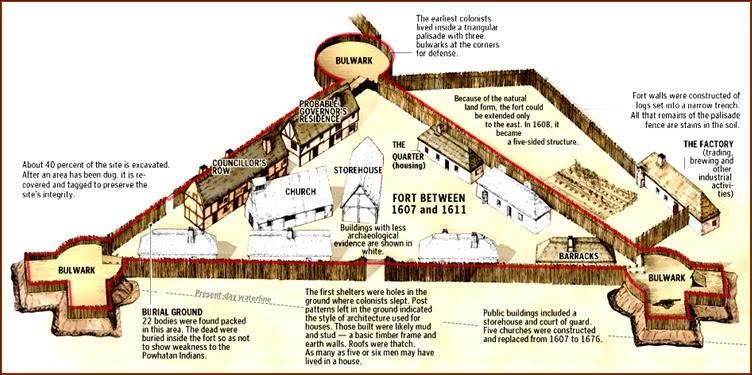
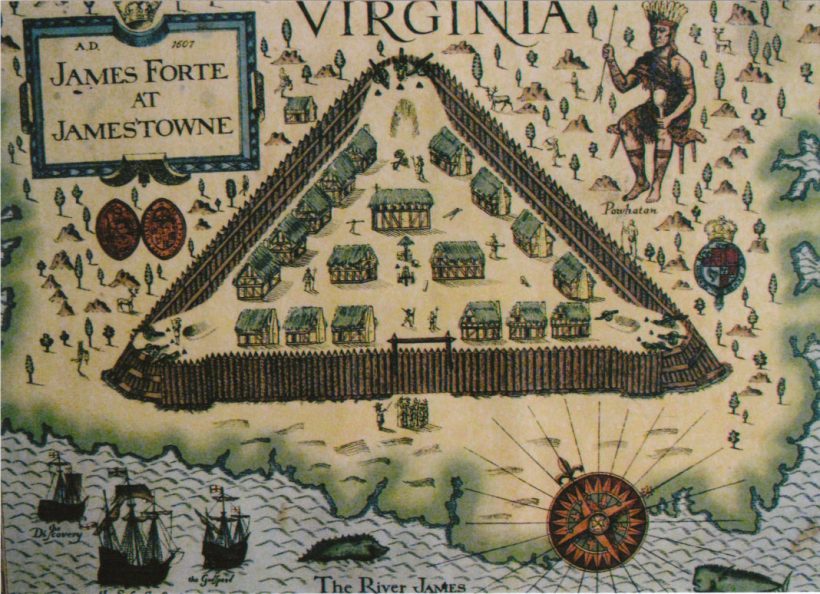 The area laid out in the royal charter was named Virginia, after both the organizing Virginia Company of London and Queen Elizabeth, “the Virgin Queen.” Founded in 1607, the first settlement – a small triangular fort populated by about 100 settlers at the mouth of the James River – was named after King James I. Jamestown was the first permanent English colony in the Americas.
The area laid out in the royal charter was named Virginia, after both the organizing Virginia Company of London and Queen Elizabeth, “the Virgin Queen.” Founded in 1607, the first settlement – a small triangular fort populated by about 100 settlers at the mouth of the James River – was named after King James I. Jamestown was the first permanent English colony in the Americas.
 Two men helped the colony to survive: adventurer John Smith and businessman John Rolfe. Smith, who arrived in Virginia in 1608, introduced an ultimatum: “He that will not work, shall not eat”, equivalent to the 2nd Thessalonians 3:10 in the Bible. Under this dire threat, the colonists at last learned how to raise crops and trade with the nearby Indians, with whom Smith had made peace.
Two men helped the colony to survive: adventurer John Smith and businessman John Rolfe. Smith, who arrived in Virginia in 1608, introduced an ultimatum: “He that will not work, shall not eat”, equivalent to the 2nd Thessalonians 3:10 in the Bible. Under this dire threat, the colonists at last learned how to raise crops and trade with the nearby Indians, with whom Smith had made peace.











You must be logged in to post a comment.